
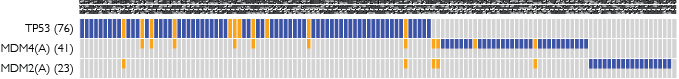
Multi-Dendrix is a software package implemented in Python for the simultaneous identification of multiple driver pathways de novo in somatic mutation data from a cohort of cancer patients. The Multi-Dendrix algorithm relies on two combinatorial properties of mutations in a driver pathway: high coverage and mutual exclusivity. Multi-Dendrix uses IBM’s CPLEX optimization software to rapidly identify an optimal collection of gene sets from genome-scale data in hundreds of patients.
| Installation | Read documentation | See examples |
| step-by-step instructions | all modules and functions | scripts and results |
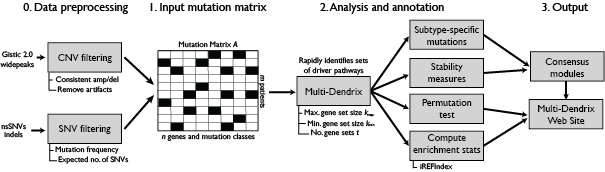
Shown above are the steps of the Multi-Dendrix pipeline. Data preprocessing is shown as a “precursor” step and at this time is not part of the Multi-Dendrix software package. Multi-Dendrix takes as input a binary mutation matrix that lists the genes mutated in each patient (for more information on input files see the File formats page). Multi-Dendrix then identifies an optimal collection of gene sets that fit the prescribed paramters, and analyzes the results for a) (sub)type-specific mutations; b) stability measures; c) statistical significance; and, d) enrichment on the iRefIndex protein-protein interaction network. Finally, the results of this analysis are output as both text and HTML. The full pipeline is described Multi-Dendrix Pipeline, and is implemented in the multi_dendrix_pipeline module.